This summer, some things will be indispensable and one of them is the Wi-Fi wireless network. Of course, Wi-Fi must be fast and the signal is stable. People have no limit to the pursuit of Wi-Fi network speed and signal, especially now that 500M and 1000M Broadband has gradually become popular. As of now, many people are yet to switch to the Wi-Fi 6 network but the newer generation Wi-Fi 7 is almost here. According to the current development trend, as soon as next summer, everyone may be able to use Wi-Fi 7.
What will change with Wi-Fi 7?
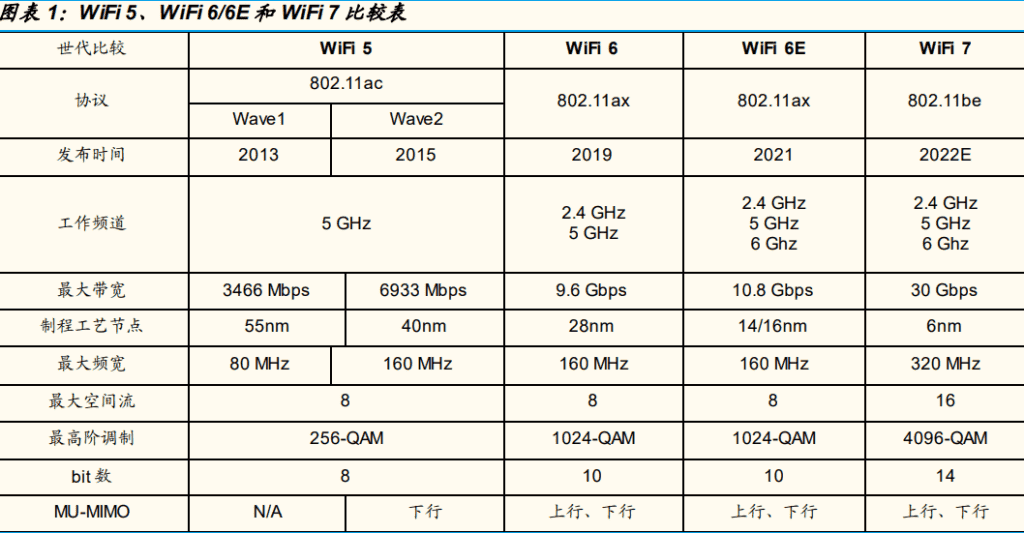
What is Wi-Fi 7? It corresponds to IEEE 802.11, which will release a new revised standard IEEE 802.11be. This is the successor of Wi-Fi 6/6E. Compared with Wi-Fi 5 to Wi-Fi 6, the upgrade only brings limited network speed improvement. Wi-Fi 6 to Wi-Fi 7 is refocused on speed, with data transfer speeds of up to 40Gbps.
What is the concept of such speed? Not to mention that most of your broadband is less than 1Gbps, even the fastest interface of the current computer, such as Thunderbolt 3/Thunderbolt 4, USB4, etc., its speed is only 40Gbps, so the speed of Wi-Fi 7 generation can really replace wired. interface.
In order to achieve such a high speed, Wi-Fi 7 also adopts a large number of new technologies. It further expands the bandwidth (up to 320 MHz), using the updated 4096-QAM modulation technology to increase the speed. It also innovatively uses new technologies such as Link and Enhanced MU-MIMO.
Wi-Fi 7 signal and delay
In addition to speed, signal and delay of Wi-Fi 7 is also a subject of concern. There are also corresponding technical solutions in Wi-Fi 7. For example, "Preamble Puncturing" can solve the problem of signal interference. Multi-chain Multi-channel operation (MLO) technology enables devices to span different frequency bands and channels, reducing latency and improving reliability.
Another important improvement of Wi-Fi 7 is that it can accommodate more users to connect to the Internet. The speed of Wi-Fi drops significantly when several users connect to the network. Now a single channel in Wi-Fi7 can accommodate more than 500 individual users which makes the connection stress-free.
To put it simply, the improvement of Wi-Fi7 is all-round. The theoretical bandwidth can already replace the wired network/interface, and the signal and delay have been further improved. Furthermore, more devices can now connect to the network while retaining its fast speeds.
The ultra-high-speed and low-latency features of Wi-Fi 7 do not only work for mobile phones and routers but also prepare for expansion in other fields, such as XR reality technology. These technologies have high requirements for delay and extremely high latency. A high refresh rate requires a high-speed network, and Wi-Fi7 can meet such high requirements.
In addition, smart cars, Internet of Things, cloud games, and the recently popular Metaverse also require Wi-Fi 7. Ultra-high network speed and stable and reliable connections are where Wi-Fi7 can play an advantage.
Although Wi-Fi 7 is good, technical challenges are not small
Wi-Fi 7 is very good and powerful, but the technical challenges it brings are also difficult. There are more challenges in the RF front-end to achieve stable and high-speed 30-40Gbps. The radio frequency front end (RFFE) is one of the three core components of the wireless communication module. It is mainly for the mutual conversion of binary signals and wireless electromagnetic wave signals during signal transmission and signal reception. In the process, the binary signal is converted into a high-frequency wireless electromagnetic wave signal. In the process of receiving the signal, the received electromagnetic wave signal is converted into a binary digital signal.
The RF front-end is mainly related to mobile cellular networks and Wi-Fi devices. According to Yole's statistics on the RF front-end market space corresponding to cellular, WiFi, and GNSS, the share of RF front-end chips related to cellular mobile communications can account for more than 80%. The market share of Wi-Fi RF front-end is about 15%. With the popularization of Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7, the importance will gradually expand.
Qualcomm - a leader in Wi-Fi technology
In the field of RF front-end chips for mobile phones, Qualcomm has achieved the world's largest revenue in 2021. It is now accelerating the expansion of the RF chip market outside of mobile phones. In the past two years, it has made frequent moves in the field of Wi-Fi, especially the popularity of Wi-Fi 6. Inseparable from the full promotion of Qualcomm, a large number of Qualcomm technologies are in the Snapdragon platform (mobile phone to the router). For example, OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6 is a Qualcomm technology.

In the current Wi-Fi 7, 4K QAM modulation technology is also the first to be standardized by Qualcomm in Wi-Fi 6. At present, Qualcomm also continues to cooperate with the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) or the Wi-Fi Alliance (WFA) to further complete Wi-Fi7 technology.
Wi-Fi 7 will be ubiquitous - Qualcomm Wi-Fi 7 ecosystem is about to bloom
The era of Wi-Fi 7 is beginning. With the comprehensive upgrade of its technical experiences such as network speed, delay and capacity, we can see Wi-Fi 7 blooming in various fields in the future, just like the popularity of 5G. In addition to enjoying high-speed Internet access on mobile phones and computers at home, we will see the existence of Wi-Fi 7 in many fields. Terminal categories such as automobiles, XR, and wearable devices will all use Wi-Fi 7 to achieve powerful wireless connections.
Of course, before the popularization of Wi-Fi 7, people still have a lot of work to do. Among them, the challenges of the RF front-end are getting bigger. If you consider the coexistence of 5G or future 6G networks, the importance of the RF front-end will become more important.






Place comments
0 Comments
You are currently seeing only the comments you are notified about, if you want to see all comments from this post, click the button below.
Show all comments